Last Updated on 9th October 2025 by Charlie Walsh
This is where the hormone responsible for all of this comes into play: testosterone. Whether you’re having sex with someone else or just yourself, you depend on testosterone (also known as T) to get — and keep — it up, from start to finish. Not only that, your T-levels affect nearly every aspect of your physical and mental wellbeing.

What is testosterone, exactly?
Testosterone (which comes from the Latin words for “testicle” and “hormone”) is the primary male sex hormone. Although it’s naturally secreted by the endocrine glands in both sexes, a healthy man’s T-levels are up to 20 times higher than a healthy woman’s. This is what gives them distinctively masculine features like facial hair, deepened voice, and increased muscle mass. Without all this testosterone, men would look (and sound) perpetually prepubescent.
Why is testosterone important?
The role testosterone plays in male health and wellbeing goes well beyond the ability to grow a bushy beard.
- It plays a powerful role in sex drive and erectile performance
- It promotes muscle growth by ramping up protein synthesis
- It bolsters bone strength
- It improves heart health and ramps up red blood cell production
- It aids in memory and cognitive function
- It’s a major mood-booster
Furthermore, it gives men a leg-up in the mating game. Higher testosterone levels increase a man’s attractiveness to potential sexual partners on a primal level — and the man will also have a stronger drive to pursue them.
What are the signs and symptoms of low testosterone?
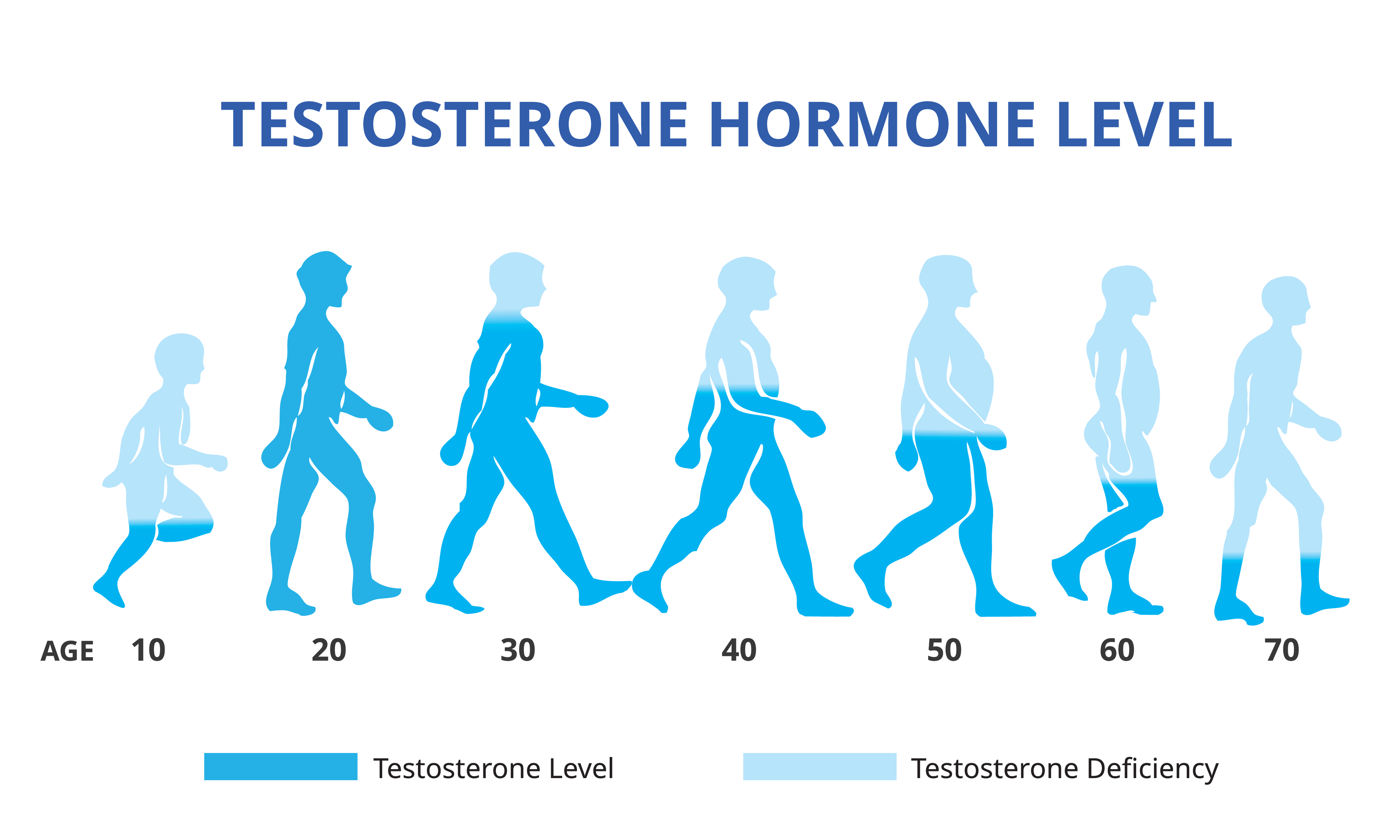
To maintain optimum health, it pays to pay attention to your T-levels. Research shows that after the age of 30, a man’s testosterone production starts dropping off, which can contribute to early signs of aging like:
- Weight gain
- Hair loss
- Depression and low energy
- Decreased bone density and muscle mass
- Memory loss
- Lower sex drive
- Reduced sperm count
- The inability to gain (and/or maintain) an erection
Does masturbation decrease testosterone?
It’s no secret that athletes have long been advised to avoid ejaculation in the final days leading up to a big game to prevent a flaccid performance on the field. Superstitions like this lead many men to wonder if their own wanking habits are to blame for their performance, both inside the bedroom and out. Turns out, there might be a kernel of truth to them after all. A small 2001 study showed that abstaining from masturbation-induced orgasm for three weeks elevated participants’ testosterone levels.
At the same time, being able to have sex in the first place is driven by testosterone, which is why men with below-average T-levels find it very hard to gain and maintain erections. Sexual climax itself temporarily boosts testosterone levels, so it stands to reason, then, that cleaning the pipes now and again (alone or with a partner) is a good way to keep your pumps primed for peak performance.
This brings us back to the question at hand: does masturbation increase testosterone, or decrease it?
Understandably, all of these conflicting answers lead to confusion, as anyone with an internet connection and an open web browser knows all too well. The answer probably lies somewhere in the middle. Studies over the years linking ejaculation and sustained serum T-levels remain inconclusive. If there’s any effect at all, it’s usually only temporary.
As with everything else in life, it’s all about balance. Masturbation is best (and indeed, most enjoyable) in moderation. If making time to masturbate is becoming central to your life and starts crowding out other interests, however, you might want to think about reeling it in a bit.
Medical perspective on masturbation and hormones
From a medical standpoint, masturbation doesn’t cause long-term dips in testosterone levels. In fact, regular sexual activity, whether solo or partnered, is generally considered part of a healthy lifestyle. Doctors often use questions about sexual habits as a window into overall hormonal health, because sudden changes in libido or erectile function can sometimes signal underlying endocrine issues. The body’s hormonal system is resilient, and fluctuations from ejaculation are short-lived, not permanent.
It’s also worth noting that testosterone levels are influenced more by age, lifestyle, and health conditions than by how often you masturbate. Chronic stress, obesity, and conditions like type 2 diabetes have a far bigger impact on T-levels than your bedroom routine. For men worried about their hormone balance, consulting a healthcare provider is the best step, as low testosterone can often be managed with lifestyle changes or medical treatment. You can read more about testosterone and men’s health on the Mayo Clinic.
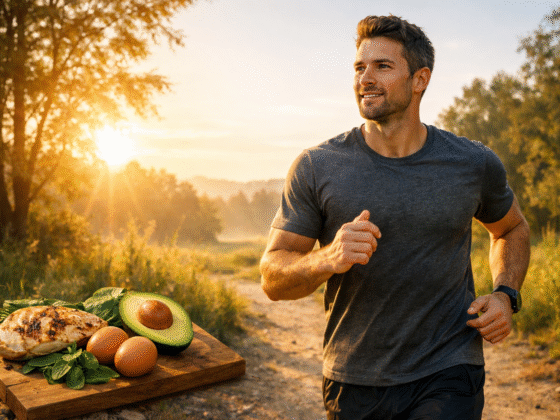
Natural Ways To Increase Testosterone
While masturbation alone might not have much of an effect on your T-levels, positive lifestyle changes certainly can — no drugs or supplements required.
Get some shuteye. Lack of sleep leads to overproduction of the stress hormone cortisol, which cancels out testosterone production.
Get a move on. Strength exercises, like deadlifts and squats, are a proven way to top up T-levels.
Get on top of your diet. Steer clear of processed foods that lead to sluggishness, and instead load up on micronutrients for maximum impact. The resveratrol in grapes and the amino acids in milk not only boost testosterone levels but also aid in sperm production. Other T-boosting foods include:
- Oily fish (salmon, sardines, tuna)
- Shellfish (oysters, crab, lobster)
- Beans (lentils, black beans, chickpeas)
- Egg yolks
- Leafy greens (kale, spinach)